Role of Trophic Cascades in an Ecosystem
http://tutor-web.net/fish/fish610.2/Lecture30/slide1-1.jpg\begin{itemize}
\item What are trophic cascades
\item Why they should be included in an EAFM framework
\item Explain how fisheries impact trophic cascades
\end{itemize}
\item What are trophic cascades
\item Why they should be included in an EAFM framework
\item Explain how fisheries impact trophic cascades
\end{itemize}
Details
http://tutor-web.net/fish/fish610.2/Lecture30/sl10-1-image.jpg\subsubsection*{Trophic Cascades and Their Importance}
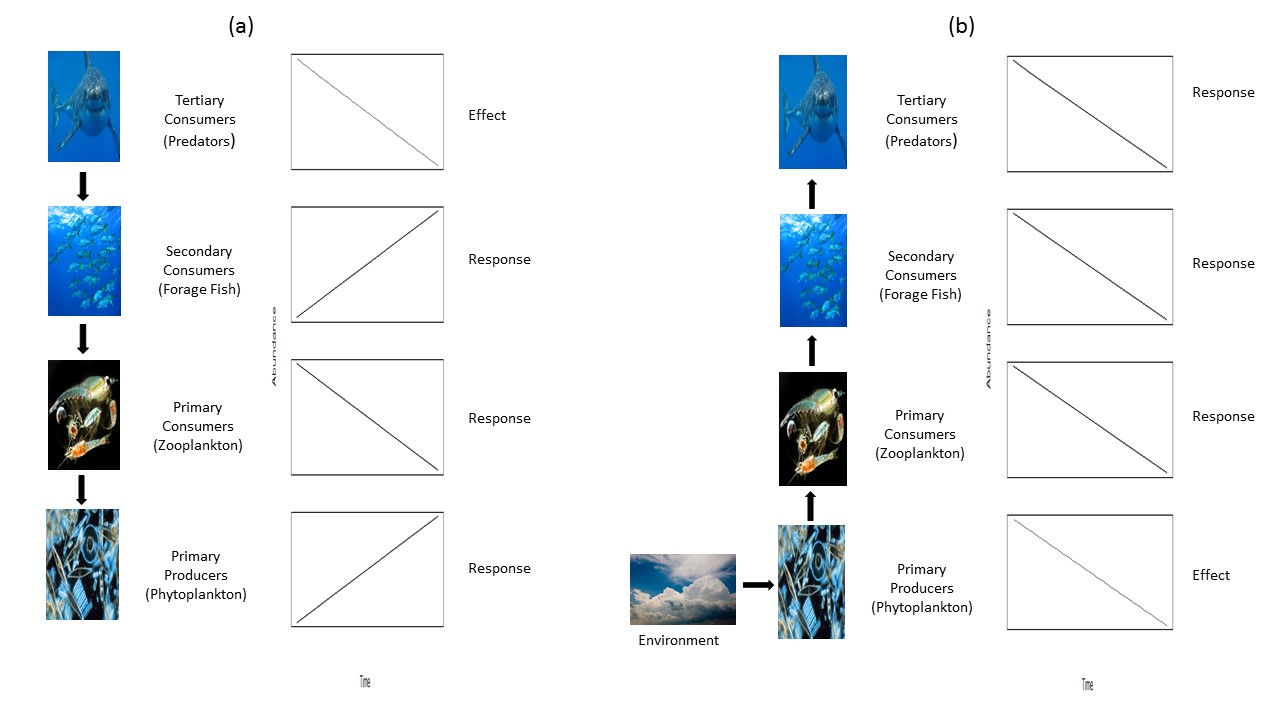
When including community considerations into an EAFM framework managers are concerned with the interactions among living organisms, i.e. how abundance changes in one species impacts the abundance of another species. Community interactions typically result from predator-prey dynamics and occur in one of two directions: bottom-up or top-down. In bottom-up cascades, the abundance of the lowest trophic level is reduced, or increased, resulting in subsequent decreases in higher trophic levels due to decreased food. In top-down cascades, the top trophic level, say secondary consumers, decreases resulting in an increase in primary consumers (decreased predators), which causes a decreases in primary producers (increased predation). These interactions are collectively referred to as trophic cascades.
\begin{defn} [Trophic Cascade]
The alteration of abundance, biomass, or productivity across trophic levels resulting from predator-prey interactions.
\end{defn}
Trophic cascades play an important ecosystem role as they can have a significant impact on fish population dynamics and can even stabilize them in alternate states \cite{cury2003functioning}. Thus, trophic cascades can result in dramatic shifts in the appearance, properties, and functionality of the ecosystem. However, trophic cascades are fluid in that they exhibit variation in their strength and duration. As a result, for each ecosystem of interest, the community interactions within it must be well understood to fully express their impact on the ecosystem.
\subsubsection*{Fisheries and Trophic Cascades}
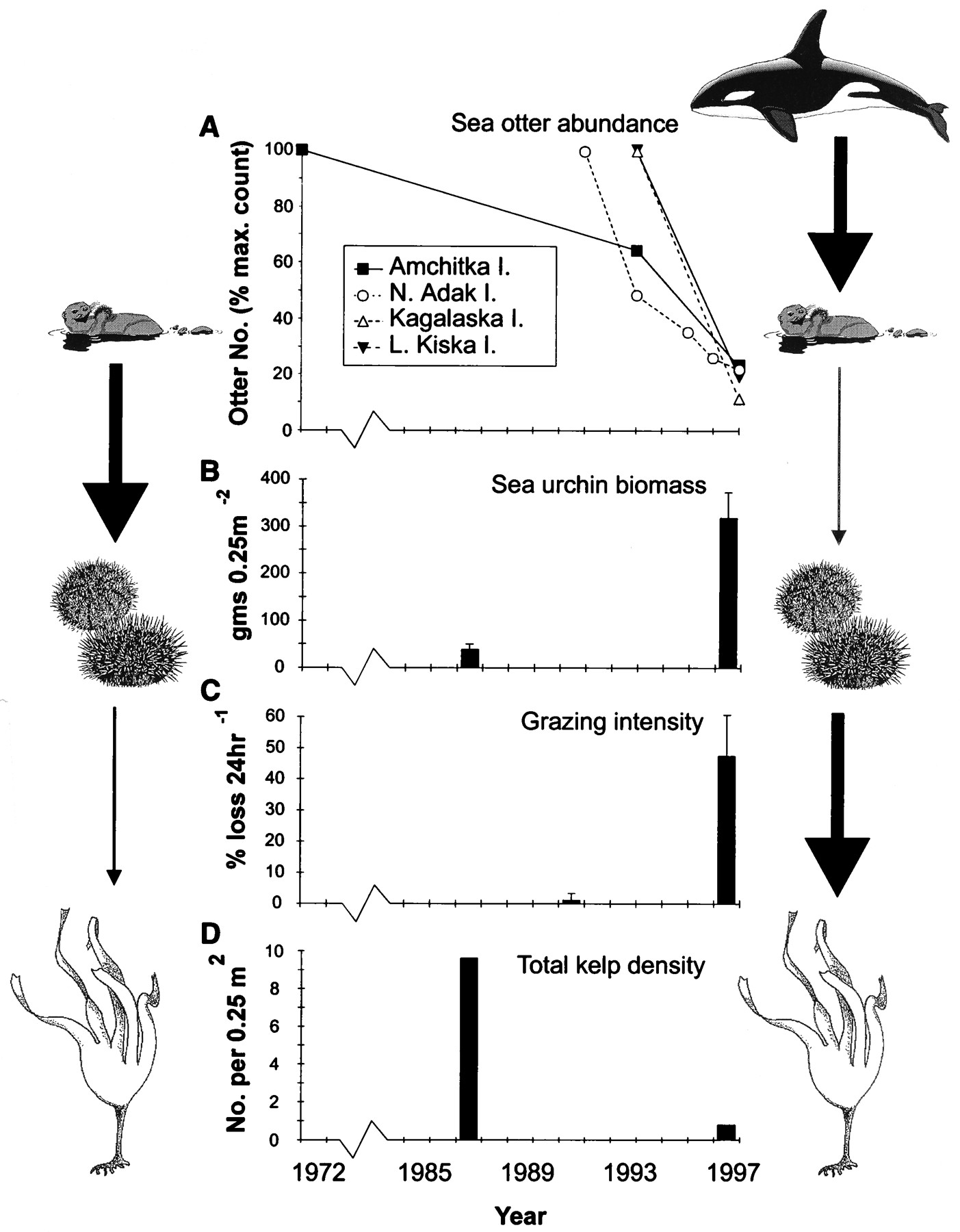
Commercial fisheries often act as a driver for top-down trophic cascades. As previously discussed, commercial fisheries tend to disproportionately harvest large, top-predators reducing the abundance/biomass of the higher trophic levels. As a result, fisheries have begun focusing more on lower trophic levels in a phenomenon known as "fishing down marine food webs (FDFW)". FDFW is quite pervasive since high trophic levels tend to be K-selected species and are therefore more susceptible to overfishing.
When including community considerations into an EAFM framework managers are concerned with the interactions among living organisms, i.e. how abundance changes in one species impacts the abundance of another species. Community interactions typically result from predator-prey dynamics and occur in one of two directions: bottom-up or top-down. In bottom-up cascades, the abundance of the lowest trophic level is reduced, or increased, resulting in subsequent decreases in higher trophic levels due to decreased food. In top-down cascades, the top trophic level, say secondary consumers, decreases resulting in an increase in primary consumers (decreased predators), which causes a decreases in primary producers (increased predation). These interactions are collectively referred to as trophic cascades.
\begin{defn} [Trophic Cascade]
The alteration of abundance, biomass, or productivity across trophic levels resulting from predator-prey interactions.
\end{defn}
Trophic cascades play an important ecosystem role as they can have a significant impact on fish population dynamics and can even stabilize them in alternate states \cite{cury2003functioning}. Thus, trophic cascades can result in dramatic shifts in the appearance, properties, and functionality of the ecosystem. However, trophic cascades are fluid in that they exhibit variation in their strength and duration. As a result, for each ecosystem of interest, the community interactions within it must be well understood to fully express their impact on the ecosystem.
\subsubsection*{Fisheries and Trophic Cascades}
Commercial fisheries often act as a driver for top-down trophic cascades. As previously discussed, commercial fisheries tend to disproportionately harvest large, top-predators reducing the abundance/biomass of the higher trophic levels. As a result, fisheries have begun focusing more on lower trophic levels in a phenomenon known as "fishing down marine food webs (FDFW)". FDFW is quite pervasive since high trophic levels tend to be K-selected species and are therefore more susceptible to overfishing.